Are you tired of flickering lights in your bathroom every time you use the hairdryer? Or maybe you’re worried about the outlet near the kitchen sink after a recent shock? These are clear warning signs that your kitchen and bathroom wiring might not be up to code, and ignoring them could have serious consequences.
Proper electrical wiring in kitchens and bathrooms is absolutely crucial, not just for convenience, but for your safety and the efficiency of your home. These rooms are high-risk areas due to the presence of water, making them prone to electrical hazards. Outdated or poorly installed wiring can lead to shocks, fires, and even electrocution. Furthermore, inefficient wiring can waste energy, leading to higher electricity bills and a bigger carbon footprint. Ensuring your wiring meets current electrical codes protects your family, your property, and your wallet. Let’s dive into understanding those codes and how to implement them safely.
Here are some actionable tips to ensure your kitchen and bathroom wiring are safe and up to code: Install GFCI Outlets: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets are essential in kitchens and bathrooms. They constantly monitor the current flowing through a circuit and quickly shut off the power if a ground fault (leakage of current) is detected. This prevents potentially fatal electric shocks. Replace standard outlets near sinks, showers, tubs, and countertops with GFCI outlets. Plan Your Circuit Layout: Kitchens, in particular, require multiple circuits to handle the heavy load of appliances like refrigerators, ovens, microwaves, and dishwashers. A dedicated 20-amp circuit is generally required for the refrigerator, and separate circuits are recommended for countertop appliances. Bathrooms need dedicated circuits for hair dryers, curling irons, and space heaters. Properly planning your circuit layout prevents overloading and tripping breakers. Use the Right Wire Gauge: The size of the wire (gauge) determines its current-carrying capacity. Using the wrong wire gauge can lead to overheating and fire hazards. Consult the electrical code and a qualified electrician to determine the appropriate wire gauge for each circuit in your kitchen and bathroom. For example, 12-gauge wire is commonly used for 20-amp circuits, while 14-gauge wire is used for 15-amp circuits. Follow Proper Grounding Procedures: Grounding provides a safe path for electricity to flow in the event of a fault, minimizing the risk of electric shock. Ensure all outlets, fixtures, and appliances are properly grounded according to the electrical code. DIY Precautions:If you choose to tackle electrical work yourself, always turn off the power to the circuit at the breaker box before starting any work. Use insulated tools, wear rubber gloves, and double-check your connections. If you're unsure about any aspect of the job, it's always best to consult a qualified electrician.
Kitchen Wiring: Code Compliance and Best Practices
The kitchen is often the heart of the home, but it's also a high-demand electrical zone. Understanding the specific electrical codes for kitchen wiring is vital for safety and functionality. Not only must you think about outlets and appliances, but also about lighting and overall load.
Dedicated Appliance Circuits
Kitchens require dedicated circuits for major appliances. These circuits ensure that high-power devices receive the necessary amperage without overloading other circuits. Here’s a breakdown: Refrigerator: A dedicated 20-amp circuit is generally required. Oven/Range: Typically requires a 240-volt circuit, rated at 40 or 50 amps depending on the appliance. Microwave: A dedicated 20-amp circuit is recommended. Dishwasher: A dedicated 15 or 20-amp circuit is required. Small Appliances (Countertops):At least two 20-amp small appliance branch circuits (SABCs) are required to serve countertop outlets. These circuits should serve no other outlets.
These dedicated circuits minimize the risk of tripped breakers and ensure reliable appliance operation.
GFCI Protection in the Kitchen
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) protection is crucial in kitchens due to the proximity of water and electrical outlets. GFCI outlets are designed to quickly shut off power in the event of a ground fault, preventing electric shock. Here’s where GFCI protection is required in kitchens: Countertop Outlets: All outlets serving kitchen countertops must be GFCI protected. Outlets within 6 feet of a sink: Any outlet located within 6 feet of the outside edge of a sink must be GFCI protected. Dishwasher Outlets:While the appliance itself often has built-in GFCI protection, it's a good practice to ensure the outlet serving the dishwasher is also GFCI protected.
Installing GFCI outlets in these areas significantly reduces the risk of electrical shock.
Lighting Circuits
Proper lighting is essential in a kitchen for both safety and aesthetics. Here’s what you need to know about kitchen lighting circuits: General Lighting: A dedicated circuit for general lighting is recommended. This circuit can serve recessed lights, ceiling fixtures, and under-cabinet lighting. Under-Cabinet Lighting: Consider using energy-efficient LED under-cabinet lighting to illuminate countertops and workspaces. This lighting can be connected to the general lighting circuit. Dedicated Lighting: Consider dedicated lighting for specific task areas like islands or breakfast nooks. Dimmers: Using dimmer switches for kitchen lighting allows you to adjust the brightness and create different moods. However, make sure the dimmer switch is compatible with the type of lighting you are using (e.g., LED-compatible dimmers).
People Also Ask: Can I add an outlet to my kitchen circuit?
Adding an outlet to an existing kitchen circuit is possible, but it’s crucial to ensure the circuit can handle the additional load. Overloading a circuit can lead to tripped breakers and potential fire hazards. It’s best to consult a qualified electrician to assess the existing circuit's capacity and determine if adding an outlet is safe. They can also advise on whether a new dedicated circuit is required.
People Also Ask: What type of wiring should I use in my kitchen?
The type of wiring you use in your kitchen depends on the specific application and the local electrical code. Non-metallic sheathed cable (NM cable), commonly known as Romex, is often used for general wiring. However, certain areas, such as those exposed to moisture or mechanical damage, may require conduit or other protective measures. Consult an electrician to ensure you are using the correct type of wiring for your kitchen.
People Also Ask: How often should I inspect my kitchen wiring?
Regularly inspecting your kitchen wiring is essential for identifying potential problems early. Look for signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked insulation, or loose connections. It's also a good idea to check for overloaded circuits and tripped breakers. A professional electrical inspection should be conducted at least every 3-5 years to ensure your kitchen wiring is safe and up to code.
Bathroom Wiring: Safety and Code Requirements
Bathrooms present unique electrical challenges due to the high moisture levels. Understanding and adhering to bathroom wiring codes is essential for preventing electric shock and ensuring safety.
GFCI Protection in Bathrooms
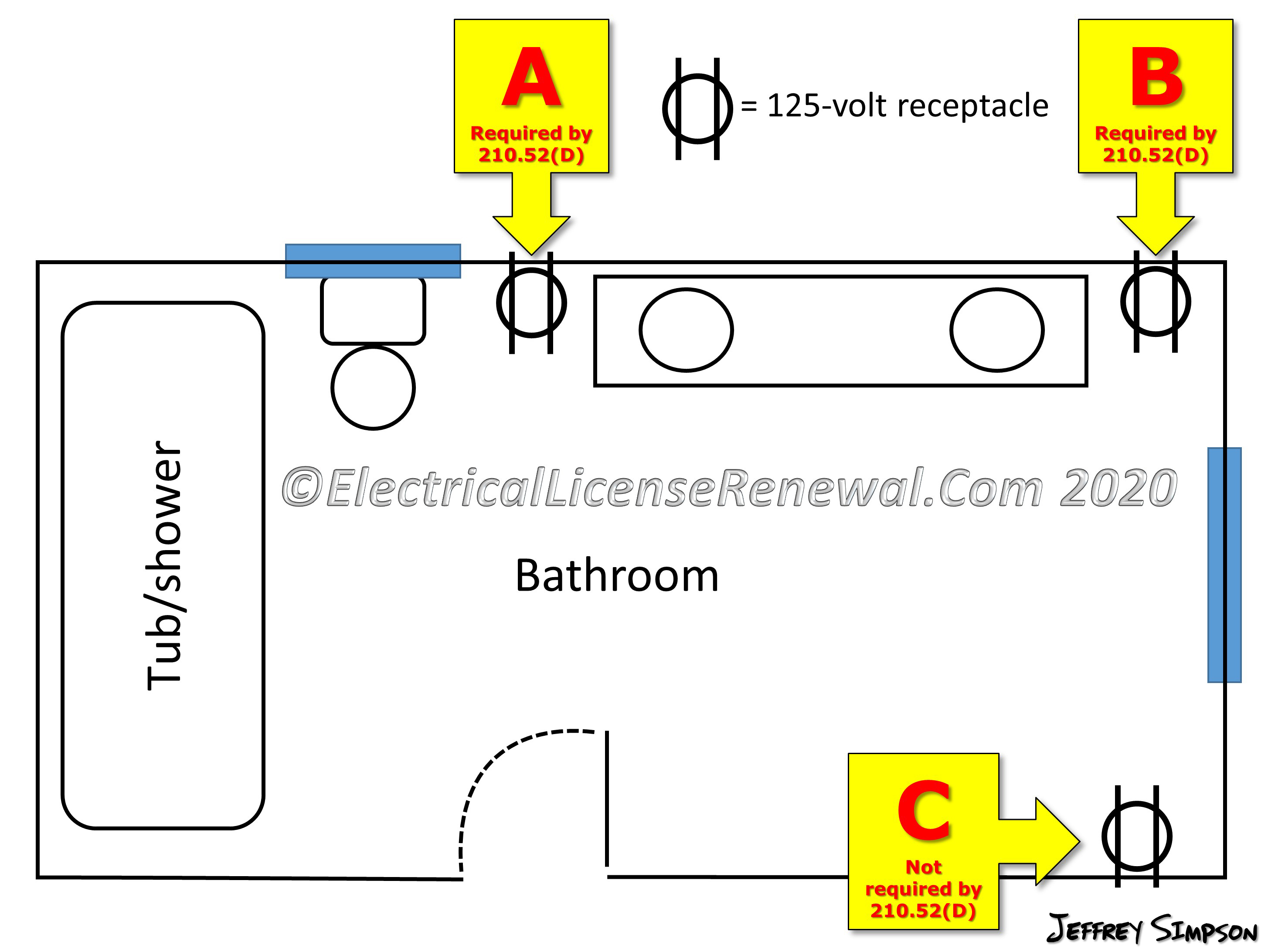
GFCI protection is paramount in bathrooms. GFCI outlets are required in the following locations: All Bathroom Receptacles: All 120-volt, 15- and 20-amp receptacles installed in bathrooms must be GFCI protected. Outlets within 6 feet of a Water Source: Any outlet within 6 feet of the outside edge of a sink, shower, or tub must be GFCI protected.
Dedicated Bathroom Circuits
Bathrooms should have at least one dedicated 20-amp circuit for receptacles. This circuit should serve only the bathroom and should not be shared with other rooms. A dedicated circuit prevents overloading and ensures reliable power for appliances like hair dryers, curling irons, and space heaters.
Lighting and Ventilation
Proper lighting and ventilation are essential in bathrooms for both safety and comfort. Here are some key considerations: Lighting: Use recessed lighting, vanity lights, and shower lights to provide adequate illumination. Ensure all lighting fixtures are suitable for damp or wet locations. Ventilation: Install a bathroom exhaust fan to remove moisture and prevent mold growth. The exhaust fan should be vented to the outside of the house. Lighting and Fan Combinations:Consider using a combination light and exhaust fan unit to save space and simplify installation.
Wiring Near Showers and Tubs
Special care must be taken when wiring near showers and tubs. The following guidelines should be followed: No Receptacles Inside the Shower or Tub: Receptacles are not allowed inside the shower or tub enclosure. Lighting Fixtures: Lighting fixtures installed above the shower or tub must be rated for wet locations. Switches:Switches should be located outside the shower or tub enclosure or be pull-chain operated.
People Also Ask: Can I install a regular outlet in my bathroom?
No, regular outlets are not permitted in bathrooms. All outlets in bathrooms must be GFCI protected. Replacing a regular outlet with a GFCI outlet is a simple DIY project, but always turn off the power at the breaker box before starting any work.
People Also Ask: What is the recommended wattage for bathroom lighting?
The recommended wattage for bathroom lighting depends on the size of the bathroom and the type of lighting fixtures used. As a general guideline, aim for approximately 75-100 watts per square foot of bathroom space. Use energy-efficient LED bulbs to reduce energy consumption and extend the lifespan of your lighting fixtures.
People Also Ask: Do I need a permit for bathroom wiring?
Whether you need a permit for bathroom wiring depends on your local building codes. In many jurisdictions, a permit is required for any electrical work, including wiring upgrades and new installations. Contact your local building department to determine if a permit is required for your project. Obtaining a permit ensures that your work is inspected and meets the required safety standards.
Energy-Efficient Wiring Solutions
In today’s world, energy efficiency is a priority. Incorporating energy-efficient wiring solutions in your kitchen and bathroom can reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and minimize your environmental impact.
LED Lighting
LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting is a highly energy-efficient alternative to traditional incandescent and fluorescent lighting. LED bulbs consume significantly less energy, last longer, and produce less heat. Replace your existing lighting fixtures with LED fixtures to reduce energy consumption and improve lighting quality.
Smart Outlets and Switches
Smart outlets and switches allow you to control your electrical devices remotely and monitor energy usage. You can use a smartphone app to turn lights and appliances on or off, set timers, and track energy consumption. Smart outlets and switches can help you identify energy-wasting devices and optimize your energy usage.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
When replacing appliances in your kitchen and bathroom, choose energy-efficient models that are Energy Star certified. Energy Star appliances meet strict energy-efficiency guidelines set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These appliances consume less energy and save you money on your electricity bills.
Proper Insulation
Proper insulation can reduce energy loss and lower heating and cooling costs. Insulate walls, ceilings, and floors in your kitchen and bathroom to improve energy efficiency and maintain a comfortable temperature.
DIY Wiring Tips and Precautions
While some electrical work can be done as a DIY project, it’s crucial to prioritize safety and follow proper procedures. Here are some essential DIY wiring tips and precautions: Turn Off the Power: Always turn off the power to the circuit at the breaker box before starting any electrical work. Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to protect yourself from electric shock. Wear Rubber Gloves: Wear rubber gloves to provide an additional layer of protection. Double-Check Connections: Double-check all connections to ensure they are tight and secure. Follow the Electrical Code: Follow the electrical code and all applicable regulations. If in Doubt, Consult an Electrician: If you're unsure about any aspect of the job, it's always best to consult a qualified electrician.
Taking on electrical work requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a thorough understanding of electrical safety. While these tips can help you tackle basic electrical tasks, remember that complex or potentially dangerous work should always be left to a licensed professional.
Wiring your kitchen and bathroom according to electrical codes might seem daunting, but it's a crucial step in ensuring the safety and efficiency of your home. By understanding the requirements, following best practices, and prioritizing safety, you can confidently tackle this essential home improvement project. Remember, if you ever feel unsure or overwhelmed, don't hesitate to consult a qualified electrician. Their expertise can provide peace of mind and guarantee that your electrical work is done correctly and safely, leaving you with a functional and secure home for years to come.
Posting Komentar